Ovarian cysts are common among women during their reproductive years. These fluid-filled sacs can form on or within the ovaries, affecting women of all ages. While most ovarian cysts are harmless and often resolve without treatment, some can lead to complications, including infertility. This article explores the relationship between ovarian cysts and fertility, highlighting the types of cysts that may impact conception and the available treatment options.
Understanding Ovarian Cysts
Ovarian cysts are typically detected during routine pelvic exams or when a woman experiences symptoms such as pelvic pain, bloating, or irregular bleeding. While most cysts are benign and require no intervention, certain types can cause fertility issues. Understanding the different types of ovarian cysts and their potential effects is essential for managing reproductive health.
Keep track of your menstrual cycle and any unusual symptoms, such as pelvic pain or irregular periods, to detect potential ovarian cysts early.
Types of Ovarian Cysts That Can Affect Fertility
Ovarian cysts are broadly classified into two categories: functional cysts and pathological cysts.
Functional Cysts
Functional ovarian cysts develop as part of the normal menstrual cycle and usually resolve on their own. They include:
- Follicular cysts: Form when a follicle fails to rupture and release an egg, instead accumulating fluid.
- Corpus luteum cysts: Develop if the follicle releases an egg but fluid builds up in the corpus luteum.
These cysts are generally harmless but can sometimes cause discomfort or disrupt ovulation.
Functional cysts are sometimes called simple cysts. A simple cyst that measures less than 5 cm in diameter usually disappear on their own after a few months.
Haemorrhagic Cysts
A haemorrhagic cyst occurs when a small blood vessel in the cyst ruptures, leading to bleeding within the cyst. Symptoms may include sudden pelvic pain and irregular periods. While they often resolve without treatment, large or persistent haemorrhagic cysts may require medical intervention.
Endometriomas
Endometriomas, or “chocolate cysts,” develop due to endometriosis, where uterine-like tissue grows outside the uterus. These cysts can lead to chronic pelvic pain and infertility. Treatment may involve hormonal therapy or surgical removal, depending on severity.
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is a hormonal disorder affecting up to 10% of women of reproductive age. It leads to multiple small cysts on the ovaries, hormonal imbalances, irregular periods, and difficulty ovulating. Symptoms include:
- Irregular or absent menstruation
- Excess hair growth (hirsutism)
- Acne and weight gain
- Infertility
Although PCOS has no cure, treatments like lifestyle changes, hormonal therapy, and fertility medications can help manage symptoms and improve fertility.
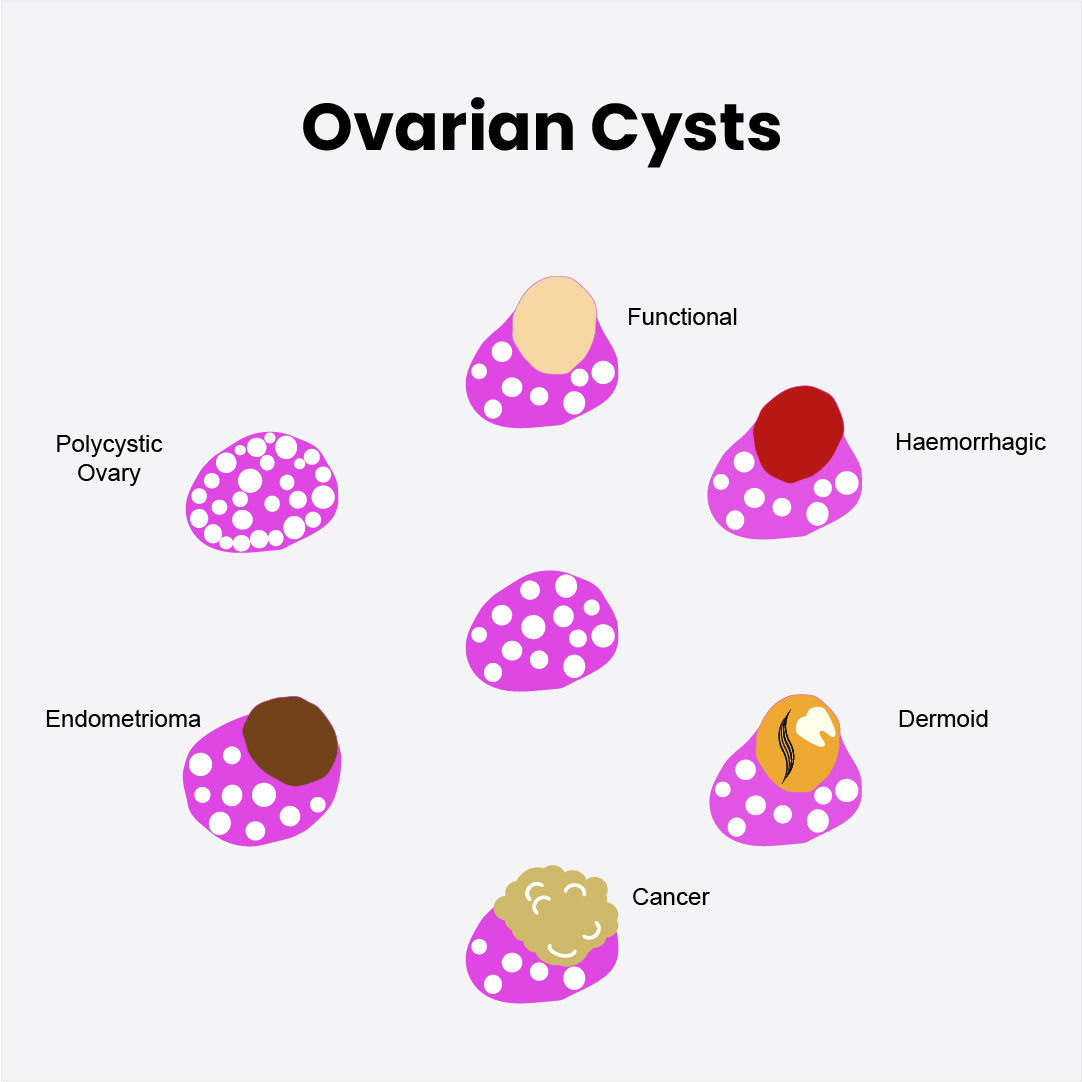
Dermoid Cysts
Dermoid cysts contain various tissue types, including hair, teeth, and skin. While typically benign, they can grow large and require surgical removal if they cause discomfort or fertility issues.
Cystadenomas
Cystadenomas are non-cancerous tumors that develop on the ovaries. Large cystadenomas may cause discomfort and fertility problems, sometimes necessitating surgical removal.
Malignant Ovarian Cysts (Ovarian Cancer)
While rare, some ovarian cysts may be cancerous. Malignant cysts are more common in older women and require prompt medical evaluation. If you have ovarian cysts, consult your doctor to rule out malignancy.
Diagnosing Ovarian Cysts
A pelvic ultrasound is the primary diagnostic tool for assessing ovarian cysts. In some cases, blood tests may be required to further evaluate cysts and rule out malignancy.
How Ovarian Cysts Impact Fertility
Ovarian cysts can affect fertility in several ways:
- Ovulation Disruption: Cysts may interfere with ovulation, preventing egg release.
- Blockage of Fallopian Tubes: Large cysts can block the passage of eggs.
- Hormonal Imbalance: Conditions like PCOS disrupt hormone regulation, affecting ovulation and menstrual cycles.
Most ovarian cysts are harmless, but certain types can affect fertility if left untreated.
Treatment Options
If an ovarian cyst is impacting fertility, treatment options include:
- Hormonal Therapy: Birth control pills or hormonal medications may regulate menstrual cycles and reduce cyst formation.
- Surgical Removal: Laparoscopic surgery may be necessary for large or persistent cysts.
- Fertility Medications: Drugs like clomiphene can stimulate ovulation in women with PCOS.
- In Vitro Fertilisation (IVF): In some cases, assisted reproductive techniques may be necessary.
Prevention and Conclusion
While ovarian cysts cannot always be prevented, maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding smoking can reduce the risk of complications. Women experiencing symptoms like pelvic pain or abnormal bleeding should seek medical advice to prevent potential fertility issues.
In conclusion, ovarian cysts can affect fertility by disrupting ovulation or blocking the egg’s passage through the fallopian tube. However, various treatment options are available to help women conceive. If you suspect ovarian cysts are affecting your fertility, consult a healthcare provider to determine the best course of action.